博弈论
Normal-form game
在博弈论中,Normal-form game是对game的一种描述。Normal-form game通过矩阵来表示game。
下图就是一个payoff矩阵: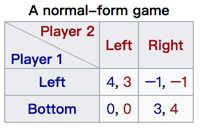
Normal-form game是一种静态模型,这个模型假设每个player仅选择一次action或策略。
Normal-form game适用于描述不需要考虑博弈进程的完全信息静态(Complete information static)博弈。
- 静态博弈
players同时进行决策 - 动态博弈
players的决策顺序有先后 - 完全信息(Complete information)
在完全信息博弈中,players的游戏结构和players的payoff矩阵是众所周知的,但players可能看不到其他players所做的所有动作。 - 完美信息(Perfect information)
在完美信息博弈中,每个player可以观测到其他players的动作,但可能缺乏关于他人的payoff或游戏结构的信息。
Extensive-form game
Extensive-form game是一种动态模型。通过使用树这种图形来表示game。不仅给出了博弈结果,还描述了博弈过程,如给出博弈中参与人的行动顺序,以及决策环境和行动空间等。
完美信息下的Extensive-form game: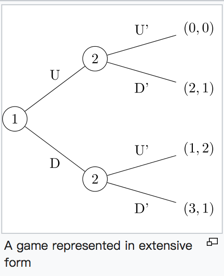
If player 1 plays D, player 2 will play U’ to maximise his payoff and so player 1 will only receive 1. However, if player 1 plays U, player 2 maximises his payoff by playing D’ and player 1 receives 2. Player 1 prefers 2 to 1 and so will play U and player 2 will play D’
非完美信息下的Extensive-form game:
信息集 是一组决策节点:
- 集合中的每个节点都只属于一个player;
- 当player到达信息集时,player不能区分信息集中的节点。即,如果信息集包含多个节点,则该集合所属的player不知道集合中的哪个节点已经到达。
下图的虚线连接的两个节点2代表player2的一个信息集,player2不知道player1采取的是U还是D。
补充:在扑克游戏中,player不知道的是对方的手牌信息而不是这个例子中的动作。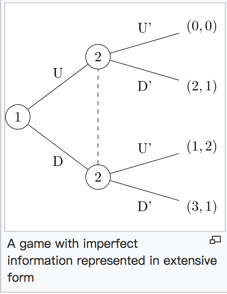
player 2 cannot observe player 1’s move. Player 1 would like to fool player 2 into thinking he has played U when he has actually played D so that player 2 will play D’ and player 1 will receive 3.
ref : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extensive-form_game
Extensive-form game和Normal-form game的转换
下图是Extensive-form game的一个例子: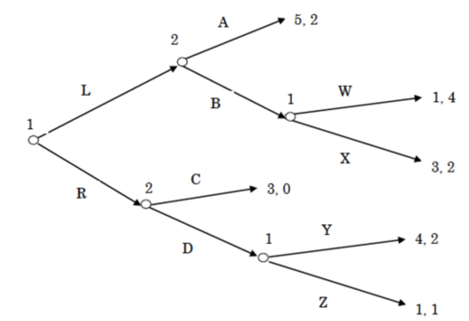
player1有三个信息集,每个信息集里面有两种行动,所以player1有8种策略;player2有两个信息集,每个信息集里面有两种行动,所以player2有4种策略。
所以转换成Normal-form game是一个横8纵4的矩阵.
FSP in Extensive-Form Games
Extensive-Form 定义扩充
- Chance
Chance被认为是一个特别的player,遵循一个固定的随机策略,决定了chance节点进入每个分支的概率分布。(如扑克游戏中的发牌)。 - Information State
我们假设游戏具有perfect recall,即每个player当前的信息状态u隐含了之前的信息状态和行动序列: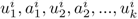
- Behavioural Strategy
在给定Information State时,动作action的概率分布。Behavioural Strategy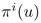 输出player i在信息状态u下,动作的概率分布。
输出player i在信息状态u下,动作的概率分布。Normal-Form 定义扩充
- Pure Strategy
player在可能遇到的所有情况下都有一个确定的动作action。(payoff矩阵中的每一行和列都是一个Pure Strategy) - Mixed Strategy
Mixed Strateg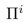 是Player i的Pure Strategy的概率分布。
是Player i的Pure Strategy的概率分布。
Fictitious Play

在normal form下:
当前策略 = 现有策略和bestResponse的加权平均。
Realization-equivalence

也就是说,Extensive-Form下的Behavioural Strategy和Normal-form下的Mixed Strategy存在一种等价。
Extensive-Form也可以使用Normal-form下的Fictitious Play来求纳什均衡解。
Extensive-Form Fictitious Play
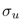 代表到信息状态u的sequence
代表到信息状态u的sequence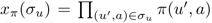
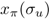 = sequence 中每个节点选择每个action的概率乘积
= sequence 中每个节点选择每个action的概率乘积

下图是对Lemma 6的一个计算的验证。

我们通过Theorem7更新Behavioural Strategy,可以收敛到纳什均衡。
具体算法XFP:
- 计算bestResponse
- 更新策略,使用Theorem7
重复上面的过程
Fictitious Self-Play
XFP会有维度灾难。generalised weakened fictitious play只需要近似bestResponse,甚至允许更新中的一些扰动。
Fictitious Self-Play:
- 使用强化学习去计算bestResponse
- 使用监督学习更新策略

样本的采集 GENERATEDAT()方法需要在理解一下。
Neural Fictitious Self-Play
强化学习和监督学习都使用神经网络去学习出一个函数。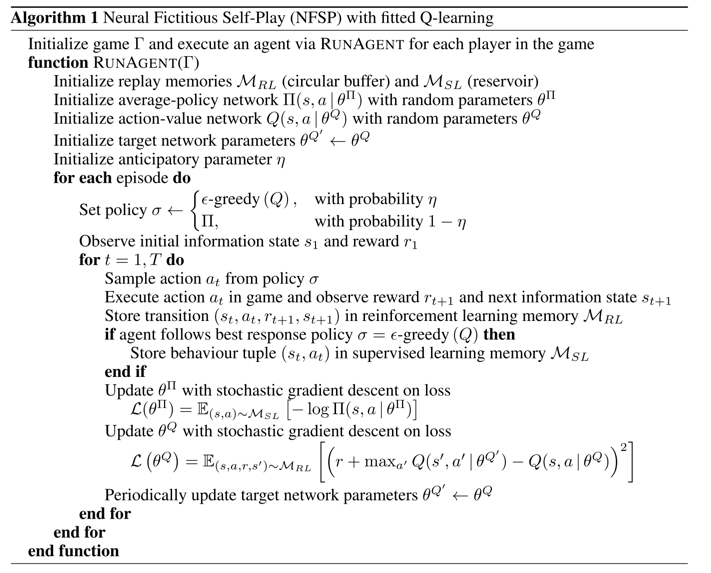
FSP中样本采集的混合策略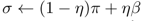 ,在NSFP中是函数,不能简单相加。
,在NSFP中是函数,不能简单相加。
转换成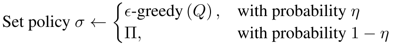 ,使用概率完成上面式子中的加操作。
,使用概率完成上面式子中的加操作。
REF:
- Topics in Algorithmic Game Theory February 8, 2010 Lecturer: Constantinos Daskalakis Lecture 2
- Fictitious Self-Play in Extensive-Form Games
- Deep Reinforcement Learning from Self-play in imperfect-information games
